The tachymeter of a watch is a horological function that often intrigues those discovering chronographs. This numbered scale, inscribed on the bezel or at the edge of the dial, is not merely decorative. It is designed to measure an average speed based on the time required to cover a known distance. The operation relies on a simple yet effective equation, allowing one to obtain a speed in kilometers per hour or miles per hour.
Contents
- What is a watch tachymeter?
- How a watch tachymeter works
- How to use a watch tachymeter
- The purpose and heritage of tachymeter watches
What is a watch tachymeter?
A watch tachymeter is a graduated scale, usually placed on the tachymeter bezel or around the dial. It is designed to measure an average speed over a fixed distance, most commonly one kilometer or one mile. The term "tachymeter" comes from the Greek tachos meaning speed and metron meaning measure, directly reflecting its primary use.
Unlike other more decorative watch complications, the tachymeter relies on a practical application of the chronograph. When a chronograph seconds hand is started at the beginning of a journey and stopped after a reference distance, the hand’s position on the tachymeter scale indicates an hourly speed. As Tag Heuer explains, if a car takes 30 seconds to cover one kilometer, the chronograph hand points to 120, corresponding to an average speed of 120 km/h.
How a watch tachymeter works
To understand the use of a tachymeter, it is necessary to consider the mathematical logic behind this scale. The tachymeter scale is constructed to directly convert a measured time into a speed expressed in units per hour.
The tachymeter formula
The formula used by a tachymeter bezel is: T = 3600 / t, where T is the speed in units per hour and t is the measured time in seconds. The number 3600 corresponds to the seconds in one hour. Thus, if a user measures the time to travel one kilometer, they can simply read the corresponding value on the scale. If the kilometer takes 30 seconds, the calculation is 3600/30 = 120, or 120 km/h.
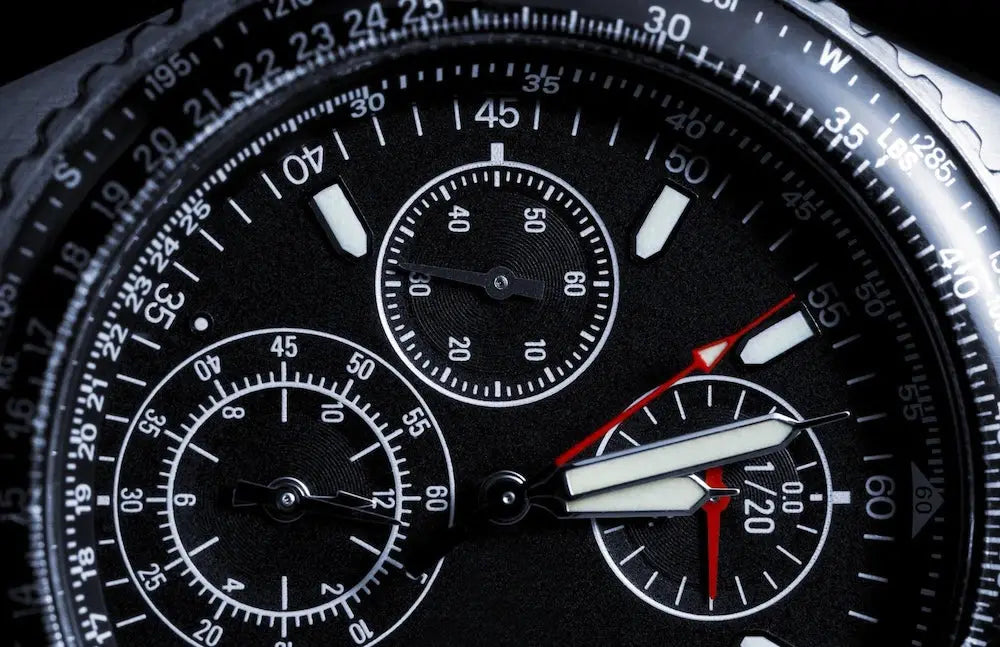
Operating range
The tachymeter scale is calibrated to work within a limited time range. Practically, it is usable for measurements between about 7 and 60 seconds. Below 7 seconds, speeds exceed 500 km/h and cannot be displayed legibly on a standard bezel. Beyond 60 seconds, speeds become too low to be indicated on the scale. This limitation is due to the logarithmic nature of the scale.
How to use a watch tachymeter

Using a tachymeter watch relies on a simple procedure linking the chronograph and the tachymeter bezel. This function becomes intuitive once the steps are understood.
Step by step
To use a watch tachymeter, first start the chronograph at the beginning of a journey corresponding to a reference distance, usually a kilometer marker. Then stop the chronograph at the end of that kilometer. The position of the chronograph seconds hand on the tachymeter bezel indicates the average speed. If the distance is covered in 45 seconds, the scale shows approximately 80, corresponding to an average speed of 80 km/h.
Other possible uses
The watch tachymeter is not limited to measuring road speed. It can also be used to calculate production rates. By measuring the time taken to produce one unit, the scale indicates an estimate of the number of units produced per hour. Some watches are also equipped with a rotating tachymeter bezel, which allows extending the measurement to longer durations or adapting it to multiple time segments.
The purpose and heritage of tachymeter watches
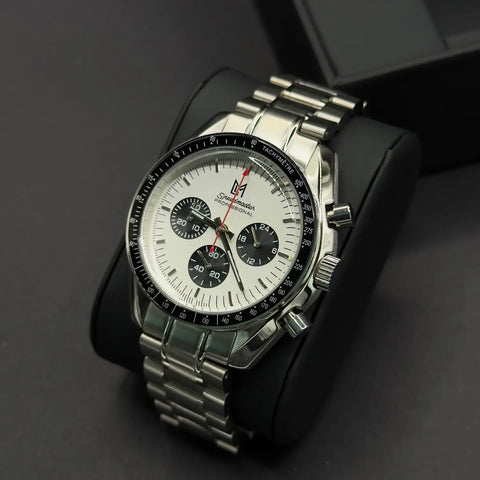

The tachymeter long served a practical role in fields such as automotive, aviation, or sports. Pilots and drivers could quickly measure their average speed using the tachymeter bezel of their chronograph.
Today, the tachymeter on a watch is less used as a technical tool, as electronic counters and GPS provide more precise measurements. However, it retains aesthetic and symbolic value in horology. Watches equipped with a tachymeter, like the Omega Speedmaster, are associated with the history of the chronograph and a sporty image, especially in pilot and racing models. This scale remains a distinctive design element of chronograph watches and preserves the heritage of an era when measuring speed to the second was a technical advantage.

Is the Miyota automatic movement a good movement?
What is the purpose of the rotating bezel on a watch?